Hot runner systems originated from non-runner systems in the injection molding industry. As an advanced plastic injection molding technology, its popularity can be traced back to the middle of the last century or even earlier. More than 50% of the moulds produced by many plastic mould factories use hot runner technology, and some mould factories even reach more than 80%.
What is a hot runner system? Why is it popular? What are this system’s advantages and disadvantages? You will learn everything in this ultimate guide.
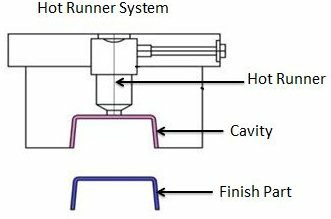
What Is a Hot Runner System?
A hot runner injection molding system is a technique that enhances the efficiency and quality of the plastic injection molding process. This technique uses a specialized system that maintains a consistent temperature in the channels (runners) leading to multiple injection points (gates) in a mold, keeping the molten plastic in a liquid state until it reaches the cavities.
How Does a Hot Runner System Work?
- Injection process initiation: The mold closes, and the plastic material is injected into the system through the nozzle of the injection molding machine.
- Hot runner system activation: The molten plastic flows through the manifold, which is a heated distribution channel, and into the individual runners that lead to each gate in the mold.
- Temperature regulation: The hot runner system is equipped with heaters and thermocouples that maintain the desired temperature in the runners and nozzles. The heaters keep the plastic in a molten state, while the thermocouples monitor and control the temperature accurately.
Why Use Hot Runner for Injection Molding?
Hot runner systems help reduce material waste and improve production efficiency by maintaining a consistent temperature in the runners and eliminating the need for solidified runners. The ability to control the flow of molten plastic results in uniform filling, reduced dimensional variations, and enhanced surface finish, leading to high-quality parts. Hot runner systems also provide greater design flexibility, allowing for complex part geometries, thin walls, and multiple gating options. They can accommodate a wide range of plastic materials, including temperature-sensitive or short-processing window materials. Additionally, hot runner systems can contribute to faster cycle times, reducing overall production time.
People often compare hot runner and cold runner systems: Understanding Hot Runner and Cold Runner Systems In Injection Molding
What Are the Purposes of A Hot Runner System?
Hot runner systems are used in injection molding to increase efficiency, enhance part quality, allow for complex designs, accommodate various materials, and reduce cycle times. These advantages have made hot runner systems a popular choice in many industries that require efficient, cost-effective, and high-quality injection molding.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Hot Runner System
Advantages of Hot Runner Systems
- Improved Efficiency: Hot runner systems eliminate the need for runners to be solidified and subsequently ejected as waste. This reduces material waste, cycle times, and associated costs. The elimination of runner removal also simplifies the overall process and reduces manual labor.
- Enhanced Quality: Hot runners allow for better control over the flow of molten plastic into the mold cavities. The consistent temperature throughout the runners ensures uniform filling and reduces variations in part dimensions and properties. It also minimizes issues such as flow lines, gate vestiges, and sink marks, resulting in higher-quality finished products.
- Expanded Design Options: Hot runner systems provide greater design flexibility as they enable the injection of multiple gates in complex and intricate part geometries. This allows for more freedom in part design, including the ability to create thin walls, intricate details, and multiple gating options, which may not be feasible with conventional cold runner systems.
- Wide Material Compatibility: Hot runner systems can accommodate a wide range of plastic materials, including those that are temperature-sensitive or have short processing windows. The ability to maintain precise temperature control allows for processing materials with specific requirements.
- Reduced Cycle Times: By maintaining the plastic in a molten state from the machine nozzle to the mold cavities, hot runner systems facilitate faster injection and cooling cycles. This helps to decrease overall production time and increase manufacturing efficiency.
Disadvantages of Hot Runner Systems
- Higher Initial Cost: Hot runner systems generally have a higher upfront cost compared to conventional cold runner systems, which can be a barrier for small-scale productions.
- Complex Design and Maintenance: Hot runner systems require more intricate design and additional maintenance compared to cold runners, which may increase complexity and maintenance costs.
- Potential for Color Change and Material Degradation: The prolonged exposure of plastic materials to high temperatures in hot runner systems can lead to color changes and material degradation, requiring careful material selection and temperature control.
- System Complexity: Hot runner systems involve additional components such as manifolds, nozzles, and heaters, which can increase the complexity of the overall injection molding setup.
- Longer Startup Time: Hot runner systems may require more time for setup and initial heating compared to cold runners, which can impact overall production time.
5 Types of Hot Runner Systems
There are several types of hot runner systems commonly used in injection molding. Here are some of the main classifications:
- Open Hot Runner System: In an open hot runner system, the runners are not enclosed within the mold plates. The molten plastic flows directly from the machine nozzle into the mold cavities through open runners. This type of system is often used for simple and small molds where cost and ease of maintenance are important.
- Valve Gate Hot Runner System: Valve gate hot runner systems use individual valve gates to control the flow of molten plastic into the mold cavities. Each gate has a mechanical or pneumatic valve that opens and closes to start and stop the flow. This allows for precise control over the injection process, minimizing gate vestige and allowing for clean gate removal. Valve gate systems are commonly used for high-quality parts with cosmetic requirements.
- Sequential Valve Gate Hot Runner System: A sequential valve gate system is an advanced variation of the valve gate system. It enables the sequential filling of multiple gates in the mold, allowing for more complex part designs.
- Insulated Runner Hot Runner System: Insulated runner systems consist of insulated channels that deliver heat to the mold cavities. The insulated runners help minimize heat loss and maintain a consistent temperature, resulting in improved energy efficiency and reduced cycle times. These systems are commonly used for large molds or molds requiring long flow distances.
- Hot Sprue Bushing Hot Runner System: Hot sprue bushing systems feature a heated sprue bushing that connects the machine nozzle directly to the mold cavity. The molten plastic flows through the heated sprue bushing, eliminating the need for a separate manifold. This type of system is suitable for simple molds with few cavities and is often used for large parts.
These are just a few examples of hot runner system types. Each system offers unique benefits and is chosen based on factors such as part complexity, quality requirements, mold design, and material characteristics. Manufacturers and molders select the most appropriate hot runner system based on the specific needs of their injection molding projects.
What Is the Application of Hot Runner?
Hot runner systems find applications across various industries due to their ability to improve production efficiency, reduce material waste, and enhance part quality. Here are some key applications of hot runner systems:
Automotive Industry
Hot runners are widely used for manufacturing automotive components such as:
- Interior parts (door panels, dashboards, consoles)
- Exterior parts (bumpers, mirror housings, trim pieces)
- Under-the-hood components (engine covers, air intake manifolds)
The consistent melt delivery and reduced cycle times offered by hot runners are crucial for high-volume automotive part production.
Medical and Pharmaceutical
Hot runners enable the production of precise and intricate parts used in medical devices and pharmaceutical packaging, such as:
- Syringes, inhalers, and drug-delivery devices
- Surgical instruments and implantable devices
- Pharmaceutical bottles, vials, and closures
The ability to mold with minimal gate vestiges and high dimensional accuracy makes hot runners ideal for these critical applications.
Consumer Products
Hot runners are extensively used for manufacturing consumer products like:
- Electronic devices and components (housings, connectors)
- Household appliances and kitchenware
- Toys and recreational products
- Personal care products (combs, brushes)
The reduced waste, shorter cycle times, and improved aesthetics from hot runner molding benefit high-volume consumer product manufacturing.
Packaging Industry
Hot runners are essential for efficient production of various packaging products, including:
- Bottle caps, closures, and lids
- Thin-walled containers and crates
- Packaging trays and blister packs
The ability to mold multiple cavities simultaneously with minimal waste makes hot runners economical for packaging applications.
Hot Runner Design Guide and Considerations
To ensure that the injection molding project implements a hot runner system that is efficient, reliable, and successful, it’s important to consider when designing a hot runner mould.
Part and Mold Design
Understand the part design, including wall thickness, gating requirements, and any unique features. Consider the mold design, such as the number of cavities and their layout. Ensure that the hot runner system design aligns with the specific requirements of the part and mold.
Material Selection
Consider the type of plastic material to be used and its specific processing requirements. Different materials have varying temperature sensitivities, flow characteristics, and processing windows. Choose a hot runner system that is compatible with the selected material and can provide precise temperature control.
Flow Analysis and Balancing
Conduct a flow analysis to identify potential flow-related issues. Optimize the runner and gate design to achieve balanced flow and consistent filling across all cavities. Consider the use of flow control elements like flow restrictors or valve gates to ensure balanced filling.
Temperature Control
Determine the required temperature profile for the hot runner system based on the material properties and processing conditions. Ensure that the system can maintain the desired temperature consistently throughout the runners, nozzles, and gates.
Thermal Expansion and Cooling
Account for the thermal expansion of the hot runner system components during operation. Allow sufficient space for expansion to prevent damage or interference with the mold. Consider cooling channels or cooling elements in the hot runner system design to dissipate heat and maintain proper temperature control.
Maintenance and Serviceability
Design the hot runner system with ease of maintenance in mind. Ensure that the system components are accessible for cleaning, maintenance, and potential repairs.
Supplier Collaboration
Work closely with a reputable hot runner system supplier or manufacturer. Engage in open communication and collaborate to design a system that meets the specific requirements of your injection molding project. Leverage their expertise and experience to ensure the optimal design and functionality of the hot runner system.
Get a deep understanding of runner design: Injection Mold Runner Design: Optimizing Molding Process Manufacturing
Selecting Your Hot Runner System
Choosing the right hot runner system for a specific injection molding project involves considering various factors. Here are some key considerations to help guide the selection process:
- Evaluate the complexity of the part design.
- Consider the type of plastic material to be used in the injection molding process.
- Determine the desired part quality and surface finish.
- Assess the expected production volume and cycle time requirements.
- Evaluate the ease of maintenance and serviceability of the hot runner system.
- Consider the budget allocated for the hot runner system.
- Research the reputation and track record of hot runner system suppliers. Look for suppliers with a proven history of delivering reliable systems and providing good customer support.
By carefully considering these factors and conducting thorough research, you can select the hot runner system that best meets the specific requirements of your injection molding project, ensuring optimal performance, part quality, and cost-effectiveness.
Conclusion
To sum up, a hot runner injection molding system provides notable benefits in terms of efficiency, part quality, design flexibility, and material compatibility. However, it is crucial to take into account factors such as initial cost, complexity, material degradation risks, and longer setup time when designing and implementing a hot runner system. By thoughtfully considering these factors and collaborating closely with a trusted supplier, the hot runner system can be designed and fine-tuned to meet the particular requirements of the injection molding project, ensuring efficient and high-quality production.
Related FAQs of Hot Runner Systems
A semi hot runner system strikes a balance between the complexity and cost of a fully hot runner system and the material waste of a cold runner system. It partially heats the runner path to keep the plastic molten, reducing waste while being simpler and more cost-effective than fully heated systems.
- A hot runner system keeps the entire runner path heated to maintain the plastic in a molten state until it enters the mold cavities.
- A hot sprue, also called a hot sprue bushing, is a heated inlet at the start of the runner system that connects the injection molding machine's nozzle to the mold.
The hot runner is a more advanced and complex system compared to just having a hot sprue in a cold runner mold.
The materials used for hot runner systems need to meet several key requirements such as high thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and toughness to withstand the harsh molding conditions. The most commonly used materials for hot runner components are:
- Tool steels: H13 tool steel, S7, 420 stainless steel, etc.
- Copper alloys: Beryllium copper (BeCu), chromium-zirconium copper (Cr-Zr Cu)
- Nickel alloys: Inconel, Monel, and Hastelloy