The Working Principle of Injection Molding
The injection molding working principle is that the plastic is heated and melted in the heating barrel of the injection moulding machine, and then the melt is pushed into the cavity of the closed mold by the plunger or reciprocating screw. It not only can produce high-precision, high-quality products under high productivity but also has a wide variety of processed plastics and wide uses. Therefore, injection molding is one of the important molding methods in plastic molding processing.
Types of Injection Molding
Scientific injection molding principles can help you achieve the process from raw materials to products. Here are four common types:
Plastic injection molding: a process in which heated molten plastic is injected into a mold, cooled and solidified, and finally molded into the desired product
Rubber injection molding: a process in which preheated rubber material is injected into a closed mold and vulcanized at high temperature and high pressure to form the desired product.
Overmolding: a process used to make plastic parts with two or more materials. For example, by adding rubber to a handle to improve grip.
Insert molding: a process that starts with placing an insert component (usually metal) into the mold before the resin enters. The material is then injected and flows around the insert to form the final part. For example, parts for metal threads.
Injection Molding Material
The following are common materials for injection molding
| Material | Key Characteristics | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| ABS | Good rigidity, toughness, easy to process | Electronic housings, automotive parts, toys |
| PC | High strength, transparent, impact resistant | Covers, safety glasses, connectors |
| PP | Lightweight, chemical resistant, fatigue resistant | Household goods, food containers, car parts |
| PE | Flexible, corrosion resistant, good insulation | Plastic bags, pipes, bottles |
| PA | High strength, wear resistant, heat resistant | Gears, bearings, mechanical components |
| POM | High strength, wear resistant, heat resistant | Gears, bearings, mechanical components |
| PS | Easy to mold, transparent, low cost | Disposable cutlery, packaging, electronics |
| TPE | Adjustable softness, good hand feel, recyclable | Seals, soft-touch parts, grips |
| TPU | High elasticity, abrasion resistant, optional transparency | Shoe soles, phone cases, sports goods |
| TPV | Heat resistant, aging resistant, automotive-grade | Auto seals, overmolded parts |
Colorants and Resin Additives for Injection Molding
Injection molding resins are typically available in black or natural colors, which can appear white, beige, or amber. Semi-custom colors are achieved by adding colorants, though slight swirls or streaks may occur. Additives like glass or carbon fibers enhance strength and reduce creep; minerals like talc lower cost and warpage; PTFE and MoS₂ improve self-lubrication; UV stabilizers and antistatic agents enhance outdoor and electronic performance. Each additive tailors resin properties to meet specific application needs.
The Plastic Injection Molding Process
1. Basic functions of injection molding machine
Plastic injection molding parts are common produced by injection molding machines. The basic functions of injection molding machine working principle are:
① Heat the plastic to reach a molten state;
② Apply high pressure on the melt to inject it and fill the cavity.
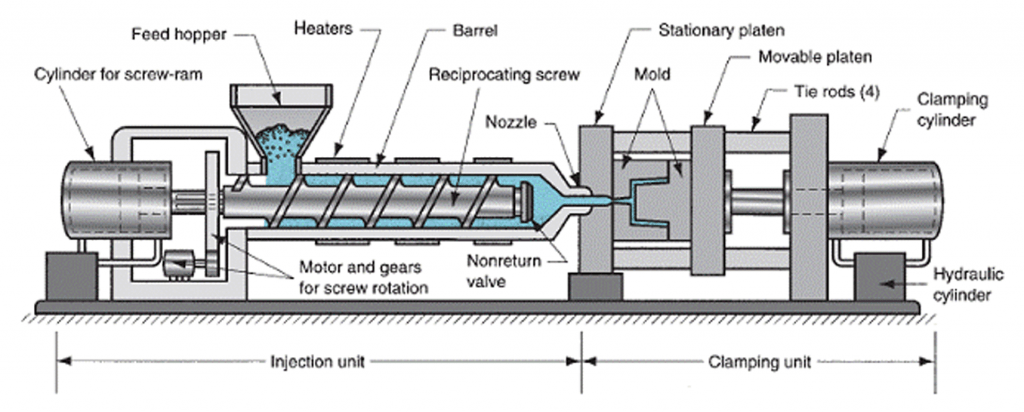
2. Injection Molding Components/Equipment
The plastic molding operation of thermoplastics is generally composed of plasticizing, filling, compacting, and cooling. The needed equipment is a custom plastic china molding machine, which is composed of injection mold tooling and auxiliary equipment (such as material drying),such as:
Barrel
Gates
Heaters
Hopper
Mold
Mold Cavity
Movable platen
Nozzle
Pellets
Reciprocating screw
Runners
Sprue
3. Injection Molding Principles
Introduction to injection molding working principles: The injection device mainly realizes the functions of plasticizing, metering, injection, and pressure maintaining and shrinking in the process of high precision plastic injection molding. The screw injection device is the most used, it is made by unifying the screw plasticizing and injection plunger into one screw.
In essence, it should be called a coaxial reciprocating rod injection device. When it is working, the plastic in the hopper falls into the heating barrel by its weight. Through the rotation of the screw, the plastic moves forward along the screw groove. At this time, the material is heated by the external heater of the heating barrel, and inside cutting the temperature rises to a molten state.
With the storage of materials at the front end of the heating barrel, the reaction force (back pressure) generated by these materials pushes the screw backward, and the limit switch is used to limit the amount of retreat. When it retracts to a certain position, the screw stops rotating, which (Measurement) is determined by the amount of injection at one time.
After the material in the mold is cooled, once the product is taken out, the mold is closed again to enter the injection molding process. At this time, the hydraulic cylinder (injection cylinder) of the injection device exerts a force on the screw, and the screw becomes an injection rod under high pressure. The melt is injected into the mold from the nozzle.
How Injection Molding of Components Working Principle?
The screw injection device comprises a screw, barrel, nozzle, and driving device. The injection screw is generally divided into three stages: feeding, compression, and metering, with a compression ratio of 2 to 3 and a length-to-diameter ratio of 16 to 18. When the melt is ejected from the nozzle because the injection force on the pressurized melt is afraid of the reaction force, a part of the melt will flow back to the rear through the screw groove. To prevent this phenomenon, a check valve is installed at the end of the screw. For rigid PVC, a conical screw head is used.
The barrel is the part that contains the screw, which is heat-resistant. Made of high-pressure resistant steel. Install an array of electric heating coils on the periphery of the barrel to heat the material in the barrel, and use a thermocouple to control the temperature so that the plastic has an appropriate temperature.
The nozzle is the transition part connecting the barrel and the mold, and an independent heating ring is installed on it because it is an important part that directly affects the melting of the plastic. Generally, open nozzles are used for injection molding for low-viscosity polyamides and a needle valve nozzle is used.
The rotation of the drive screw can be driven by an electric motor or a hydraulic motor, and the reciprocating movement of the screw is realized by hydraulic pressure.
The parameters of the injection molding machine characterized by the injection device:
- The injection volume refers to the maximum amount that the injection molding machine can inject into the mold each time, which can be expressed by the quality of the injected polystyrene melt or the volume of the injected melt;
- The injection pressure refers to the pressure exerted on the section of the barrel during injection; the injection speed refers to the moving speed of the screw during the injection.
4. Mold Clamping Device Working Principle
In addition to completing the opening and closing actions of the mold, the mold clamping device’s main task is to resist the high pressure of the melt injected into the mold with sufficient force to lock the mold. Do make it closed.
Regardless of whether the clamping mechanism is mechanical or hydraulic, it should be flexible, punctual, fast, and safe. From the technological requirements, the opening and closing of the mold must have a buffer effect, and the running speed of the template should be fast and then slow when the mold is closed, and slow first and then continue to slow when the mold is opened. To prevent damage to molds and injection molding machine parts and functions.
The force applied to the mold to keep the mold closed during the injection molding process is called the clamping force, and its value should be greater than the product of the cavity pressure and the projected area of the China injection parts (including the runner). The average pressure in the cavity is generally between 20~45Mpa.
Since the clamping force line reflects the size of the molded product area of the injection molding machine, the maximum clamping force of the injection molding machine is often used to indicate the specifications of the injection molding machine, but there is also a roughly proportional relationship between the clamping force and the injection volume. However, the clamping force representation method does not directly reflect the size of the injection product, or it is not convenient to use. Many manufacturers worldwide use clamping force/equivalent injection volume to indicate the specifications of injection molding machines. For injection volume, to have a common comparison standard for different machines, the theoretical injection volume when the injection pressure is repeated 100Mpa is specified, that is equivalent injection.
Volume=theoretical injection volume*rated injection pressure/100Mpa.
5. Control System
The injection molding machine hydraulic control system is mainly divided into a conventional hydraulic control system, a servo control system, and a proportional control system. Due to the complexity of the hydraulic system, a proportional valve oil circuit system is an example to illustrate the outline. The characteristic of this system is: that there is a proportional element (electromagnetic proportional flow valve or electromagnetic proportional flow directional valve, electromagnetic proportional pressure valve) that controls the flow and pressure in the oil circuit system.
Through the proportional action of the external given electric simulation signal and the magnetic force, the opening amount of the valve core or the spring force of the valve core is controlled to control the system flow or pressure, to achieve the proper injection speed, screw speed, opening and closing speed and injection pressure, holding pressure, screw torque, injection seat thrust, ejection force, mold protection pressure implemented in single-stage, multi-stage control or step-less control.
Looking for a High-Efficiency Injection Molding Process Supplier?
At the heart of efficient production lies a deep understanding of injection molding principles. With years of hands-on experience, our team knows how material behavior, mold design, and process parameters interact — ensuring each part is molded with precision, consistency, and minimal waste. From flow simulation to optimized cooling, we apply scientific injection molding principles to every project, helping you bring products to market faster, with better quality and lower cost.