Thermoset vs Thermoplastic, are two major plastic materials in the injection molding process. Even though thermoset plastic and thermoplastic are similar, they have key differences. Sometimes, thermoplastics are the better choice, and other times thermosets are better. So, it is important to know the differences between thermoset and thermoplastic and to make smart decisions.
This guide will introduce those two plastics and analyze their advantages and disadvantages. Join us to get a clear understanding of thermoset and thermoplastic materials, and help you choose the right one for your project.
What is Thermosets Plastic?
Thermoset plastics, also known as thermosetting polymers, are essential materials characterized by their permanent hardness after molding. Thermoset plastics undergo a chemical reaction during molding, resulting in a rigid and infusible structure. This curing process typically involves heating or the addition of a curing agent, which initiates cross-linking between polymer chains, creating a strong three-dimensional network that cannot be remelted or reshaped once set. Common examples include epoxy and phenolic resins. Thermosetting is one type of polymer plastic. Having a deeper understanding in polymer types, please read our blog: Understanding Polymer Types: Comparing Plastics and Elastomers
Thermoset Plastic Chemical Makeup
At the core of thermoset plastics is a network of polymer chains held together by strong cross-links. The key feature is the presence of reactive sites within the polymer molecules that allow for the formation of these cross-links.
Thermoset Plastic Molecular Structure
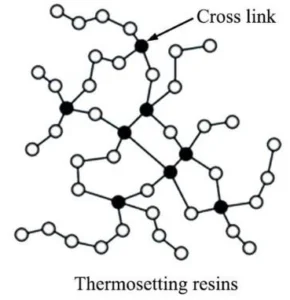
The molecular structure of thermoset plastics is characterized by a three-dimensional network. As the material undergoes the curing process, the polymer chains link together, creating a rigid and durable structure. The cross-linking structure contributes to the exceptional heat resistance and dimensional stability of thermoset plastics. Once set, they cannot be remolded or reshaped, making them ideal for applications where durability and high-temperature performance are paramount.
Common Thermoset Plastic Materials
Here are some common thermosetting plastics that are widely used by manufacturers:
- Phenolics
- Silicone
- Melamine
- Epoxy
- Polyvinylidene
- Fluoride (PVDF)
- Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)
- Polyurethane
- Polyimide
Advantages and disadvantage of Thermoset Plastic
The cross-linked structure of thermosets determines their key properties, and understanding the strengths and weaknesses of these materials helps make informed decisions when selecting materials and appropriate molding processes.
| Advantage Point | Explanation |
|---|---|
| High Durability & Rigidity | Hard and shape-retaining after curing; ideal for stable structures. |
| Excellent Heat Resistance | Withstands high temperatures; used in automotive, aerospace, electronics. |
| Good Chemical Resistance | Resists acids and solvents; suitable for harsh environments. |
| Great Electrical Insulation | Ideal for electrical components and insulators. |
| High Strength & Stiffness | Strong and rigid; fits structural applications. |
| Excellent Moldability | Can form complex shapes during curing. |
| Adhesive Properties | Some resins (e.g., epoxy) bond well with various materials. |
| Design Flexibility | Custom formulations possible for specific needs. |
| High Strength-to-Weight Ratio | Strong yet lightweight; important for aerospace and automotive use. |
| Disadvantage Point | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Non-Recyclable / Non-Remoldable | Cannot be reshaped after curing; limits recyclability. |
| Poor Thermal Conductivity | Inefficient at dissipating heat; may cause overheating in electronic parts. |
| Brittleness | Can easily break under impact or sudden mechanical stress |
What is Thermoplastic?
Thermoplastics represent a class of polymers characterized by their unique chemical composition and structural properties. Thermoplastics can be melted and reshaped multiple times without undergoing a chemical change. Examples of thermoplastics include polyethylene and polypropylene. The common molding process for thermoplastics involves heating the material to a molten state, shaping it, and then cooling it to solidify the desired form.
Thermoplastic Chemical Composition
At the core of thermoplastic materials is a long-chain polymer molecule. These polymer chains consist of repeating monomer units linked together through covalent bonds. The chemical composition varies based on the specific type of thermoplastic. Common types include polyethylene, polypropylene, polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polystyrene, and many others.
Thermoplastic Molecular Structure
The molecular structure of thermoplastics is characterized by linear or branched polymer chains. Unlike thermosets, these chains do not form a three-dimensional network with strong cross-links. In their natural state, thermoplastics are solid, but they soften when heated and return to a solid state upon cooling.
Common Thermoplastic Materials
Here are some common thermoplastic materials widely used in various industries:
- Acrylic
- Nylon
- Acetal Copolymer Polyoxymethylene
- Acetal Homopolymer Polyoxymethylene
- Polycarbonate (PC)
- Polyethylene (PE)
- Polystyrene (PS)
- Polypropylene (PP)
- Polyvinylchloride (PVC)
- Polyethylene terephthalate (PET)
- Teflon
Zhongde has produced injection molding plastic parts in thermoplastic, click to view our previous products.
Advantages and Disadvantage of Thermoplastic
The thermoplastic molecular structure determine their advantages and disadvantages in practical applications.
| Advantage Point | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Resists chemicals and corrosive environments. |
| Recyclable & Reshapeable | Can be remelted and reshaped multiple times. |
| Chipping Resistance | Durable and resistant to surface damage. |
| Good Electrical Insulation | Suitable for electrical and electronic applications. |
| Anti-Slip Properties | Some types offer enhanced grip and slip resistance. |
| Eco-Friendly | Recyclable and supports sustainable practices. |
| Excellent Impact Resistance | Withstands mechanical stress; good toughness. |
| Better Aesthetic Finishing | Can be molded into smooth, attractive finishes. |
| Good Adhesion to Metals | Bonds well with metal parts in hybrid components. |
| Disadvantage Point | Explanation |
|---|---|
| UV Degradation | May degrade under prolonged sunlight exposure. |
| Heat Sensitivity | Softens or melts at high temperatures. |
| May Be More Expensive | Sometimes costlier than thermoset plastics. |
Major Difference Between Thermosetting and Thermoplastic
Although thermoplastics and Thermosets are similar plastic polymers in some cases, there are some differences between thermosetting and thermoplastic. We will discuss these differences under the following aspects:
Different in Molding Process
In the field of plastic molding, there are significant differences between thermosetting plastics and thermoplastics in terms of molding methods, processing characteristics, and application areas. Understanding the distinctions between these two types of plastics helps in selecting the most suitable material and molding process for practical production. The following table summarizes the key differences in molding methods between thermosetting plastics and thermoplastics, providing a reference for choosing the appropriate plastic material.
| Characteristic | Thermoplastics | Thermosets |
|---|---|---|
| Heating & Molding | Softens or melts when heated; can be molded by injection, extrusion, blow molding, etc. | Undergoes chemical crosslinking when heated; molded by compression, transfer, or hot pressing. |
| Reprocessability | Can be reheated and remolded multiple times. | Once molded, cannot be remelted or reprocessed. |
Different in Physical Properties
Thermoset:
- Rigidity: Generally rigid and hard after curing.
- Strength: Often exhibits high strength and dimensional stability.
- Heat Resistance: Excellent heat resistance due to the stable cross-linked structure.
- Chemical Resistance: Good chemical resistance, particularly against solvents and corrosive substances.
Thermoplastic:
- Flexibility: Can vary from flexible to rigid depending on the specific type.
- Strength: Strength may vary, and some thermoplastics may have lower tensile strength compared to thermosets.
- Heat Resistance: Moderate heat resistance; softening and melting occur within a defined temperature range.
- Chemical Resistance: Varies among different thermoplastics, with some exhibiting good chemical resistance.
Different in Applications
Thermoplastics: The uses of thermoplastics vary from industry to industry. Since thermoplastics are resistant to chemical attacks such as corrosion, they are a good alternative to metals. They are widely used in industries such as medical and biomedical, chemical, plumbing, automotive, food and beverage, electronics, and construction.
Some of the applications of thermoplastics include:
- Industrial machinery parts
- Electrical packaging and insulation materials
- Laboratory equipment
- Non-stick pans
- Gas tanks
- Piping systems

Thermosets: Some industries choose thermosets because they are more economical and meet product specifications. The ease of forming complex geometries and the ability to withstand high temperatures are also reasons for choosing thermosets.
Thermoset applications include:
- Electronic housings
- Chemical processing equipment such as pipes, battery covers and accessories
- Panels, housings and doors
- Medical components
- Vehicle components and parts

Different in Aesthetics
Thermoset: Typically exhibits a smooth and polished surface finish after molding. Can be used for applications where aesthetic appearance is important.
Thermoplastic: Surface finish may vary depending on the molding process and specific type of thermoplastic. Can achieve a wide range of textures and finishes, offering flexibility in aesthetic design.
Different in Cost Consideration
Generally, thermosets are more expensive than thermoplastics.
Thermoset: Due to the more complex curing process, tooling costs, equipment costs, and labor costs can be higher.
Thermoplastic: Generally lower cost due to the less complex molding process and faster production cycles.
Thermoset vs Thermoplastic: Which Material is the Best?
Selecting the right plastic material is important for ensuring the performance and durability of your products. Both thermoplastic and thermosetting plastic offer a wide range of options. The choice between thermoplastic and thermoset is based on the specific requirements of your desired product.
If your application demands resilience in the face of high temperatures, thermosetting plastics are the preferred choice. Thermoset plastics excel in environments where heat resistance, structural integrity, and chemical resistance. On the other hand, if your product is working in corrosive materials and requires ease of production at competitive pricing, thermoplastics would be better. Thermoplastics are ideal for crafting high-volume parts with complex shapes, making them metal alternatives. Moreover, their recyclability and reusability contribute to long-term cost savings.
The material selection process involves careful consideration of factors such as impact resistance, strength, and heat resistance. Choosing the wrong material can impact the functionality of even the best-designed product. Therefore, when you choose plastic materials, looking for professional assistance is important. Their expertise can guide you in making the informed choice for your specific application, ensuring the success and longevity of your products in the real world.
Related post: Plastic Material Selection Guide for Your Manufacturing Process
Zhongde is Your Best Injection Molding Partner
In conclusion, the choice between thermoplastic and thermosetting plastic materials is an important decision that influences the performance and functionality of your products. Both thermoplastic and thermoset offer a wide of options, each excelling in specific applications.
If you are in trouble with plastic material selection, Zhongde is ready to offer help. Zhongde has professional engineers who will analyze your product design and help you select the suitable plastic materials for your project. Zhongde provides custom plastic injection molding with advanced injection molding machines and injection mold tools. We will offer high-quality injection molding services and custom plastic products at competitive prices. Welcome contact Zhongde if any requirements.
FAQs of Thermosets VS Thermoplastic
In general terms, thermoset plastics are often perceived as having high strength and dimensional stability compared to thermoplastics. Thermoset plastics, after undergoing the curing process, develop a strong network of crosslinks that contributes to their rigidity and dimensional stability. Thermoplastics can soften when heated and typically lack strong crosslinking.
Thermoplastics, in general, are not toxic. The toxicity of a thermoplastic material depends on the specific type of plastic, its composition, and any additives or processing agents used in its production. Most commonly used thermoplastics, such as polyethylene, polypropylene, polyvinyl chloride (PVC), and others, are considered safe for use in various applications.
The full form of PVC is polyvinyl Chloride. It is thermoplastic.
In addition to being heat resistant, thermoset plastics also have a highly flexible design, good dimensional stability, and are much more cost-effective than thermoplastics.




