Home » Copper
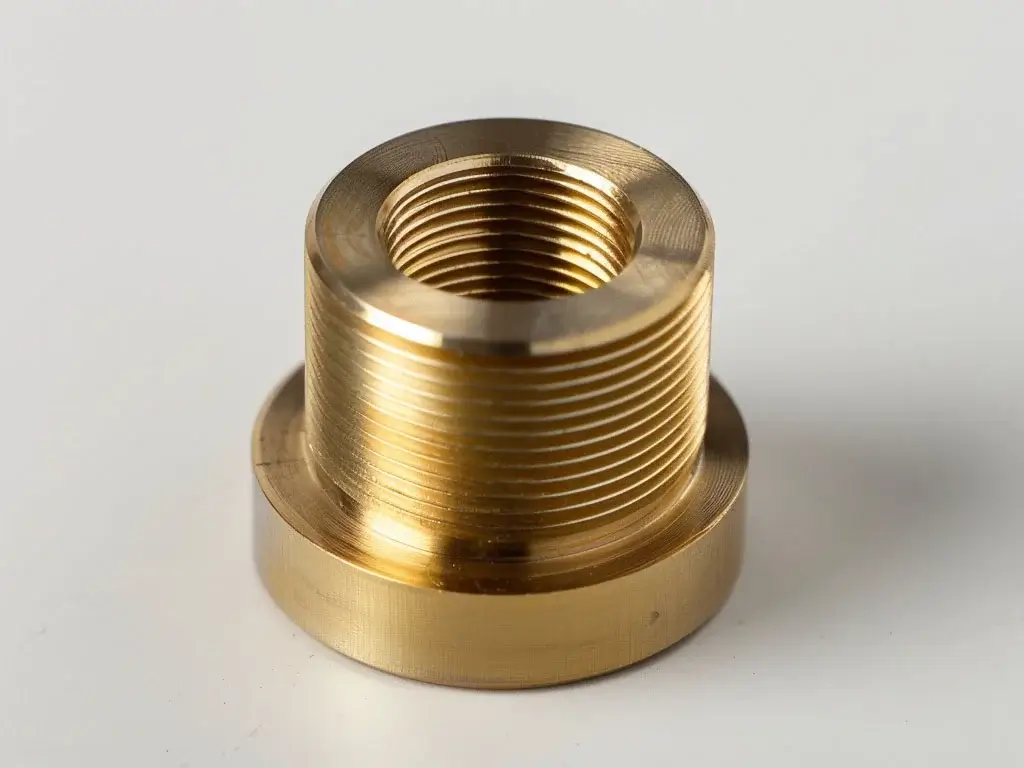

Copper
Material Type
Metal
Process Compatibility
CNC Machining, Metal Stamping
List of Metal Material
List of Plastic Material
List of Elastomer & Rubber Material
Copper Description
Price
$$$$$
Strength
Excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, malleability, and antimicrobial properties.
Weakness
Susceptibility to oxidation, tendency to tarnish over time, and softer than some other metals.
Common Application
Electrical wiring and cables, plumbing pipes and fittings, roofing materials, heat exchangers and radiators.
Available Copper Materials
Copper 101
Copper 101, also known as oxygen-free copper (OFC), is characterized by its high electrical conductivity and exceptional purity. It contains minimal oxygen content, typically less than 0.001%, which enhances its electrical and thermal conductivity properties.
| Tensile Strength | Elongation at Break | Hardness | Desnsity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 69-365 MPa | 5-55% | 65-90HB | 8.89-8.94 g/cm³ |
Copper 110
Copper C110, also known as electrolytic tough pitch (ETP) copper, is distinguished by its high conductivity and excellent thermal properties. It exhibits exceptional electrical conductivity, making it ideal for electrical wiring, conductive components, and electrical busbars.
| Tensile Strength | Elongation at Break | Hardness | Desnsity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 69-365 MPa | 5-50 % | 65-90 HB | 8.89 g/cm³ |
Get Copper Parts with Zhongde
Can copper be used for electrical wiring?
Copper is commonly used for electrical wiring due to its excellent electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance.
What are the benefits of using copper in plumbing?
Stainless steel is available in a range of surface finishes, including brushed, polished, matte, and textured finishes, each offering distinct aesthetic and functional characteristics.
What factors affect the conductivity of copper?
The conductivity of copper is primarily influenced by its purity, temperature, grain size and structure, alloying elements, and mechanical stress. Higher purity copper generally exhibits better conductivity, while temperature changes and mechanical stress can affect conductivity levels. Additionally, factors like grain size and alloying elements play a role in modifying copper's conductivity.